JOIN TODAY STUDENTS OF KV BOUDH and GOURI SHANKAR PUBLIC SCHOOL. CONTACT- 9437335465, 9124187885, 8658640143, 9853416563
Thursday, 25 August 2016
Thursday, 18 August 2016
CLASS VII SCIENCE SA I -ACID BASE AND SALT BY RABI SIR
CLASS VII SCIENCE SA I -ACID BASE AND SALT BY RABI SIR
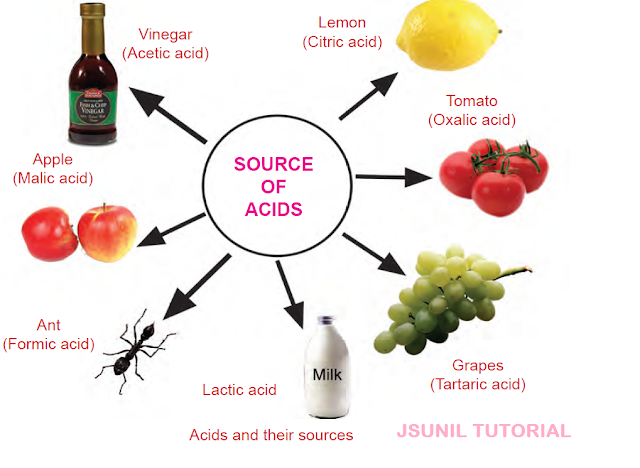
Q1. What are acids?
Ans. Acids are the substances which are sour in taste.
Q2. What are bases?
Ans. Bases are the substances which are bitter in taste & soapy to touch.
Q3.Give examples of acids and bases.
Ans. Acids- hydrochloric acid, acetic acid, citric acid, lactic acid etc
Bases- baking soda, sodium hydroxide, soap etc
Q 4. Name the acids present in the following substances.
Q5. What are indicators? Give examples.
Ans. Indicators are the special type of substances which are used to distinguish between acids & bases by showing colour changes.
Example: litmus, turmeric, beetroot, China rose extract, phenolphthalein etc.
Q6.Name the source from which litmus is obtained.
Ans. Litmus is obtained from a plant lichens.
Q7. in what forms is litmus available?
Ans. Litmus is available in the form of solution or in the form of strip of paper.
It is available as red & blue litmus.
Q8. Why do we use indicators?
Ans. We use indicators to find out whether a substance is acidic, basic or neutral, as all the substances can’t be tasted. Some of the substances are highly corrosive and hence can be harmful to us if tasted.
Q9.What happens when phenolphthalein is added to (a) Acidic solution (b) basic solution (c) Neutral solution
Ans.
(a) in acidic solution, the colour of phenolphthalein remains colourless.
b) When phenolphthalein is added to basic solution, the colour changes to pink (magenta).
c) In neutral solution, it remains colourless.
Q10.What are neutral substances?
Ans. The substances which are neither acidic nor neutral are known as neutral solutions.
Q11. What happens when a base is put on turmeric paste? What will happen when acid is added to the same?
Ans. When base is added to turmeric paste, then its colour changes to red. If we put an acid on the same then changes to yellow again.
Q12. How will you identify weather a substance is acidic or basic using red & blue litmus?
Ans. Acids & bases can be distinguished using litmus solutions as follows:
- if the colour of red litmus changes to blue, then the substance is basic in nature.
- if the colour of blue litmus changes to red, then the substance is acidic in nature.
Q13. Ammonia is used in many household products like window cleaners. It turns red litmus to blue. What is the nature of ammonia?
Ans. As ammonia turns red litmus to blue that shows it is basic in nature.
Q14. What is the effect of China rose indicator on acidic & basic solutions?
Ans. China rose indicator turns acidic solutions to dark pink and basic solutions to green.
Q15.What is neutralization reactions?
Ans. The reaction in which an acid & a base react to form salt and water, with the evolution of heat is known as neutralization reaction.
Acid + base ------> salt + water.
Hydrochloric acid + sodium hydroxide --> sodium chloride + water
Q16. What are salts? Are they acidic, basic or neutral?
Ans. Salts are substances formed by the reaction of an acid and base. Salts can be acidic, basic or neutral.
Q17. What are antacids?
Ans. antacids are the medicines that arte use to relieve from acidity in stomach. Example: milk of magnesia, eno etc.
Q18 what causes acidity in stomach?
Ans. Our stomach contains hydrochloric acid which helps us to digest food. When the amount of acid present in stomach increases, it leads to acidity.
Q19 How is antacids helpful in relieving indigestion?
Ans. Antacids are basic in nature, hence they neutralize the effect of excess of acid and relieve us from indigestion.
Q20. Why is calamine solution put on the ant sting?
Ans. When an ant bites, it injects formic acid into the skin. The effect of acid can be neutralized by applying calamine solution which is basic in nature.
Q21.Sometimes we treat the soil with bases. Give reasons why?
Ans. Excessive use of fertilizers makes the soil acidic, which is not suitable for the growth of the plants .Hence we treat the soil with bases like calcium oxide to neutralize of acid.
Q22.The factory waste is treated with basic substances before disposing it?
Ans. The wastes of factories contain acids. If they are allowed to flow into the water bodies, then they are harmful to the aquatic life. Therefore, factory waste are treated with basic solutions.
Q23.What is the chemical name of the following:
Q24. What is the chemical composition of milk of magnesia?
Ans. The chemical composition of milk of magnesia is magnesium hydroxide.
Q25. What is the chemical composition of calamine solution?

Q1. What are acids?
Ans. Acids are the substances which are sour in taste.
Q2. What are bases?
Ans. Bases are the substances which are bitter in taste & soapy to touch.
Q3.Give examples of acids and bases.
Ans. Acids- hydrochloric acid, acetic acid, citric acid, lactic acid etc
Bases- baking soda, sodium hydroxide, soap etc
Q 4. Name the acids present in the following substances.
Substance
| Acid |
Vinegar
| acetic acid |
Curd
| lactic acid |
Guava
| oxalic acid |
Lemon
| citric acid |
Amla
| citric acid |
Tamarind
| tartaric acid |
Q5. What are indicators? Give examples.
Ans. Indicators are the special type of substances which are used to distinguish between acids & bases by showing colour changes.
Example: litmus, turmeric, beetroot, China rose extract, phenolphthalein etc.
Q6.Name the source from which litmus is obtained.
Ans. Litmus is obtained from a plant lichens.
Q7. in what forms is litmus available?
Ans. Litmus is available in the form of solution or in the form of strip of paper.
It is available as red & blue litmus.
Q8. Why do we use indicators?
Ans. We use indicators to find out whether a substance is acidic, basic or neutral, as all the substances can’t be tasted. Some of the substances are highly corrosive and hence can be harmful to us if tasted.
Q9.What happens when phenolphthalein is added to (a) Acidic solution (b) basic solution (c) Neutral solution
Ans.
(a) in acidic solution, the colour of phenolphthalein remains colourless.
b) When phenolphthalein is added to basic solution, the colour changes to pink (magenta).
c) In neutral solution, it remains colourless.
Q10.What are neutral substances?
Ans. The substances which are neither acidic nor neutral are known as neutral solutions.
Q11. What happens when a base is put on turmeric paste? What will happen when acid is added to the same?
Ans. When base is added to turmeric paste, then its colour changes to red. If we put an acid on the same then changes to yellow again.
Q12. How will you identify weather a substance is acidic or basic using red & blue litmus?
Ans. Acids & bases can be distinguished using litmus solutions as follows:
- if the colour of red litmus changes to blue, then the substance is basic in nature.
- if the colour of blue litmus changes to red, then the substance is acidic in nature.
Q13. Ammonia is used in many household products like window cleaners. It turns red litmus to blue. What is the nature of ammonia?
Ans. As ammonia turns red litmus to blue that shows it is basic in nature.
Q14. What is the effect of China rose indicator on acidic & basic solutions?
Ans. China rose indicator turns acidic solutions to dark pink and basic solutions to green.
Q15.What is neutralization reactions?
Ans. The reaction in which an acid & a base react to form salt and water, with the evolution of heat is known as neutralization reaction.
Acid + base ------> salt + water.
Hydrochloric acid + sodium hydroxide --> sodium chloride + water
Q16. What are salts? Are they acidic, basic or neutral?
Ans. Salts are substances formed by the reaction of an acid and base. Salts can be acidic, basic or neutral.
Q17. What are antacids?
Ans. antacids are the medicines that arte use to relieve from acidity in stomach. Example: milk of magnesia, eno etc.
Q18 what causes acidity in stomach?
Ans. Our stomach contains hydrochloric acid which helps us to digest food. When the amount of acid present in stomach increases, it leads to acidity.
Q19 How is antacids helpful in relieving indigestion?
Ans. Antacids are basic in nature, hence they neutralize the effect of excess of acid and relieve us from indigestion.
Q20. Why is calamine solution put on the ant sting?
Ans. When an ant bites, it injects formic acid into the skin. The effect of acid can be neutralized by applying calamine solution which is basic in nature.
Q21.Sometimes we treat the soil with bases. Give reasons why?
Ans. Excessive use of fertilizers makes the soil acidic, which is not suitable for the growth of the plants .Hence we treat the soil with bases like calcium oxide to neutralize of acid.
Q22.The factory waste is treated with basic substances before disposing it?
Ans. The wastes of factories contain acids. If they are allowed to flow into the water bodies, then they are harmful to the aquatic life. Therefore, factory waste are treated with basic solutions.
Q23.What is the chemical name of the following:
Common name
|
Chemical name
|
Quick lime
|
Calcium oxide
|
Slaked lime
|
calcium hydroxide
|
Baking soda
|
sodium hydrogen carbonate
|
Q24. What is the chemical composition of milk of magnesia?
Ans. The chemical composition of milk of magnesia is magnesium hydroxide.
Q25. What is the chemical composition of calamine solution?
Ans. The chemical composition of calamine solution is zinc carbonate.
Wednesday, 17 August 2016
CLASS IX SCIENCE- SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT – I PRACTICE PAPER, 2016
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT – I PRACTICE PAPER, 2016
SCIENCE
Class – IX
[SUCCESS POINT BABUSAHI BOUDH-9437335465,9124187885,8658640143]
2.What will be the value of “g” at the pole as compared to the value of “g” at the equator?[1]
3. Distinguish between inter varietal and interspecific hybridization of crop plants? [1]
4. Identify dispersed phase and dispersing medium I the following (a)fog and (b)Cheese[2]
5. Give one word for the following [2]
(a) Group of cells with similar structure and designed to give highest efficiency function.
(b) Process of taking up a permanent shape size and function.
(c) Animal tissue connecting muscles to bones
(d) Kidney shaped cell that enclose stomata.
6. Define uniform circular motion .draw any example related to it.[2]
7. Distinguish three states of matter with respect to following properties: [3]
(a)Density (b)Diffusion (c) Partical motion
8. (a) State the difference between pure substance and mixture giving one example of each?[3]
(b)identify homogenous mixture from the following
(a) Brass ,(b) Smoke , (c) Tincture of Iodine and (d) Milk
9. Sanchit’s grandmother was not well . he took his grandmother to the hospital .Doctor suggested some blood test and urine test. He went to the diagnostic Labiratory with his grandmother for all these tests.[3] (a)Which technique is used in urine and blood test.
9. Sanchit’s grandmother was not well . he took his grandmother to the hospital .Doctor suggested some blood test and urine test. He went to the diagnostic Labiratory with his grandmother for all these tests.[3] (a)Which technique is used in urine and blood test.
(b)Mention value shown by Sanchit.
10.Identify the type of tissue (a) Bronchi of the lungs (b) Duct of salivary gland (c)The lining of mouth[3]
11. Answer these questions .[3]
(a)Why cell is called structural and functional unit of life?
(b) Why is plasma membrane is called selectively permeable membrane?
(c) name the factor which decides the movement of water across the plasma membrane.
10.Identify the type of tissue (a) Bronchi of the lungs (b) Duct of salivary gland (c)The lining of mouth[3]
11. Answer these questions .[3]
(a)Why cell is called structural and functional unit of life?
(b) Why is plasma membrane is called selectively permeable membrane?
(c) name the factor which decides the movement of water across the plasma membrane.
12. Show that the rate of thw change in momentum of an object is the product of mass and acceleration.[3]
13. (a) Does acceleration tell us about the direction of motion?
(b) A car accelerates uniformly 2m/s to 10m/s in 8 sec. .It then slows down to a final velocity of 4m/s in 6 sec. Calculate the acceleration of car during the first 8 sec. and during last 6 sec. [3]
14. Sate the reason for: [3]
(a) When a man jump out of a boat to the bank of river, the boat moves backward
(b) All the cars are provided with seat belt
(c) It is dangerous to jump out of a moving bus.
13. (a) Does acceleration tell us about the direction of motion?
(b) A car accelerates uniformly 2m/s to 10m/s in 8 sec. .It then slows down to a final velocity of 4m/s in 6 sec. Calculate the acceleration of car during the first 8 sec. and during last 6 sec. [3]
14. Sate the reason for: [3]
(a) When a man jump out of a boat to the bank of river, the boat moves backward
(b) All the cars are provided with seat belt
(c) It is dangerous to jump out of a moving bus.
15. For each given statement decide whether the statement is refferin distance or displacement.Explain your answer. [3]
(a) How far is your house from school by car?
(b) How far it is from Mumbai to Goa by airplane
(c) The length of Jhelum River?
16.Give two example of fodder crops raised as food for the livestock.
(b) State ant two advantage of using manure
17. “There has been a 4 times increase in the production of food grain from 1960 t0 2004 with only 25% increase in cultivatable land” Mention the step under taken by farmer to achieve this success. [3]
18. Mention three ways that are followed to prevent the weeds in crop field.[3]
19. (a) Describe an activity with diagram to illustrate that no change in temperature takes place when a liquid convert into vapour.
(b)Mention two difference between evaporation and boiling. [5]
20. Difrentiate between physical and chemical change and classify following into physical and chemical change
(a) How far is your house from school by car?
(b) How far it is from Mumbai to Goa by airplane
(c) The length of Jhelum River?
16.Give two example of fodder crops raised as food for the livestock.
(b) State ant two advantage of using manure
17. “There has been a 4 times increase in the production of food grain from 1960 t0 2004 with only 25% increase in cultivatable land” Mention the step under taken by farmer to achieve this success. [3]
18. Mention three ways that are followed to prevent the weeds in crop field.[3]
19. (a) Describe an activity with diagram to illustrate that no change in temperature takes place when a liquid convert into vapour.
(b)Mention two difference between evaporation and boiling. [5]
20. Difrentiate between physical and chemical change and classify following into physical and chemical change
(a) water freezes into form ice [5]
(b) Sugar dissolving in water
(c) Burning of paper
21. (i) Define tissue .What is the utility of tissue in multicellular organism?
(ii) Are plants and animal made up of the same type of tissue ? If no write three poit of difference. [5]
22. Draw velocity - time graph and prove that v = u + at . A body moving with a velocity of 2 m/s acquire velocity of 10m/s in 5 sec. Find its acceleration[5]
23. (a) newtons first law of motion is also called law of inertia ? Justify this statements.
(b) A plastic and a cricket ball are rolled on a floor with same velocity which one wil cover larger distance before stoping? Give reason.
(c) A truck of mass 1200kg is moving with velocity 72 m/h and it takes 3 sec to stop after breakes are applied .Calculate the force exerted by brakes. [5]
24. Mentin and explain two fress initiative for increasing the water available for agriculter.(b) Explain these term (i) Compost and (ii) green manure [5]
(b) Sugar dissolving in water
(c) Burning of paper
21. (i) Define tissue .What is the utility of tissue in multicellular organism?
(ii) Are plants and animal made up of the same type of tissue ? If no write three poit of difference. [5]
22. Draw velocity - time graph and prove that v = u + at . A body moving with a velocity of 2 m/s acquire velocity of 10m/s in 5 sec. Find its acceleration[5]
23. (a) newtons first law of motion is also called law of inertia ? Justify this statements.
(b) A plastic and a cricket ball are rolled on a floor with same velocity which one wil cover larger distance before stoping? Give reason.
(c) A truck of mass 1200kg is moving with velocity 72 m/h and it takes 3 sec to stop after breakes are applied .Calculate the force exerted by brakes. [5]
24. Mentin and explain two fress initiative for increasing the water available for agriculter.(b) Explain these term (i) Compost and (ii) green manure [5]
PREPARED BY RABI SIR...
CLASS IX AND X -DOWNLOAD THE SA I SAMPLE PAPERS/ PRACTICE PAPERS
DOWNLOAD THE SA I SAMPLE PAPERS/ PRACTICE PAPERS
- CBSE 2014 class 9 Social Science question paper sa-1
- CBSE 2014 class 10 maths question paper sa-1
- New 10th Hindi SA-1 Question paper added Sept. 2014-2015
- New 10th Maths SA-1 Question paper added
- New 9th Maths SA-1 Question paper added
- 9th maths CBSE SA1 Question papers Sep. 2014
- 10th SA-1 Original Social Science Question paper 2014
- Class 10 SA-1 Hindi B an A and Sanskrit Question Papers 2014 – 2015
- Class 10 SA-1 English Question Papers Conducted in different CBSE schools 2014 – 2015
- Mathematics CBSE 2014 – 2015 Class 10 SA1 Question Papers – Conducted in different CBSE schools
CLASS IX SCIENCE- FOOD RESOURCES QUESTIONS FROM CBSE PAPERS
SA-I (2013) TLPEK7V
1. Mention two climatic conditions essential for different crops for growth and completion of their life cycle. 1
Ans: Temperature and photoperiods.
2. “Green Revolution of 1960 is a boon by itself”. List three steps that may be initiated to increase crop production 3
Ans: The major groups of activities for improving crop yields can be classified as:
(a) Crop variety improvement (b)Crop production improvement (c) Crop protection management.
3. In what ways internal parasites like worms and flukes and external parasites cause harm to the cattle’s. 3
Ans: External parasite – Skin diseases; worms – affect stomach and intestine; Flukes – damage liver
4. Explain the meaning of ‘milch’ and ‘draught animals. Mention the scientific name of common Indian cow. 3
Ans: Milk-producing females are called milch animals (dairy animals) like cow , while the ones used for farm labour are called draught animals like ox,donkey.
The scientific name of common Indian cow is Bos indicus
5. (a) Differentiate between mixed cropping and inter-cropping. Give one example of each.
(b) How is crop-rotation different from the above two ?
(c) Mention the factors that are taken into consideration for deciding choice of crops for inter
cropping and crop rotation. Also mention one advantage of each of these cropping patterns.
Ans: (a) In mixed cropping two or more crops are grown simultaneously. For eg wheat + gram
Inter - cropping - two or more crops are grown simultaneously on the same field in a definite pattern. For eg, soyabean +maize
(b) In crop rotation different crops are grown on a piece of land in a pre-planned succession.
Depending upon duration of crop rotation is done for different crop combination.
(c) Inter- Cropping - crops are selected such that their nutrient requirements are different. This ensures maximum utilization of the nutrients supplied and prevents pests and diseases from spreading to all plants - thus better returns.
Crop - rotation - Availability of moisture and irrigation facilities Two or more crops can be grown in a year with good harvest
SA-I (2013) NK9FZA3
1. Mention the significance of sun hemp in the crop variety improvement process.1
Ans: Sun hemp is a green plant that turn into green manure which helps in enriching the soil in nitrogen and phosphorus.
2. What is organic farming? List its four advantages. 3
Ans: Organic farming is a farming system with minimal or no use of chemicals as fertilizers, herbicides, pesticides etc with a maximum input of organic manures.
Advantages:-
(a) Farm wastes (straw and livestock excreta) are recycled.
(b) Bio agents such as culture of blue green algal are used in the preparation of bio fertilizers.
(c) Neem leaves or turmeric is used as a bio pesticide in storage of grains.
(d) Healthy cropping systems such as mixed cropping inter cropping and crop rotation are beneficial in insect, pest and weed control besides providing nutrients.
3 (a) List three factors on which cultivation practices and crop yield depends.
(b) Name three stages involved in farming practices. 3
Ans: (a) Biotic and abiotic resistance, change in maturity duration, wider adaptability.
(b) Crop variety improvement, crop production improvement, crop protection management.
4. (a) Farmer A wants to grow fodder crops while farmer B wants to grow cereals. Mention the agronomic characteristics which the two farmer would desire in their respective crops. 5
(b) List any four other factors for which variety improvement is done.
(c) Name and define the process of incorporating desirable characteristics into crops.
Ans: (a) For fodder crop – Tallness and profuse branching and Cereal crop - Dwarfness
(b) Higher yield, biotic and abiotic resistance, changes in maturity duration, Improved quality, wider adaptability.
(c) Hybridization. : It is the process of crossing between genetically dissimilar plants.
SA-1(2014) LACWASE
1. India is a country with three fourth of the population engaged in agriculture. Even though financial conditions of some farmers do allow them to take higher level farming practices and improved agriculture technology, yet they are hesitant to use of HYV seeds with traits such as resistance to disease and pests, high quality that would results finally in higher yield. [3]
(i) What is meant by genetically modified crops ?
(ii) What are the desired agronomic characters for fodder and cereal crops ?
(iii) In your opinion what should be done so that the modern agriculture technology is adopted by most of the farmers ?
Ans: (i) To get desired traits in a crop (ii) Fodder – profuse branching, cereal – dwarfness
(iii) encourage scientific temper, awareness, use of knowledge
2. Define ‘Rain water Harvesting’ and ‘Water shed management’ and state one advantage of each. [3]
Ans: Rainwater harvesting is a technique used for collecting, storing and using rainwater for irrigation and other uses. The rainwater is collected from various hard surfaces such as roof tops and/or other manmade aboveground hard surfaces.
Watershed management: The management of water resources in an certain area. It is done to increase the utility of rainwater by building small check-dams . The check-dams stop the rainwater from flowing away and also reduce soil erosion.
3. ow does maximum utilization of available resources be ensured in composite fish farming ? Mention its limitation? Discuss how this limitation of composite fish culture can be overcome? [5]
Ans: The maximum utilization of available resources be ensured in composite fish farming by using of number of fish varieties in a single pond to prevent competition for resources. Each one must have different feeding zones.
Limitation – The major problem in fish farming is the lack of availability of good quality seed.
To overcome this problem, fishes are allowed to breed in ponds using hormonal stimulation. This has ensured the supply of pure fish seed in desired quantities.
4. what is hormonal stimulation in fish and how is it done in fish?
Ans: Hormonal stimulation of fishes is done to mature sex cells artificially. Hormones and methods used for stimulation slightly vary for different species of fishes. Hormone that could be used for stimulation is Luteinizing hormone (LH) that trigger ovulation.
5. In an experiment to test the presence of starch in a sample of food the wrong step is :[1]
(a) Take foodstuff like potato or rice
(b) Crush food in boiling water
(c) Add iodine powder in test tube (Ans)
(d) Pour mixture in the test tube
6. Rohit was trying to test the presence of starch in potato extract. He forgot the reagent with which starch gives blue black colour. Help him to select the correct stain from the following :[1]
(a) Safranin
1. Mention two climatic conditions essential for different crops for growth and completion of their life cycle. 1
Ans: Temperature and photoperiods.
2. “Green Revolution of 1960 is a boon by itself”. List three steps that may be initiated to increase crop production 3
Ans: The major groups of activities for improving crop yields can be classified as:
(a) Crop variety improvement (b)Crop production improvement (c) Crop protection management.
3. In what ways internal parasites like worms and flukes and external parasites cause harm to the cattle’s. 3
Ans: External parasite – Skin diseases; worms – affect stomach and intestine; Flukes – damage liver
4. Explain the meaning of ‘milch’ and ‘draught animals. Mention the scientific name of common Indian cow. 3
Ans: Milk-producing females are called milch animals (dairy animals) like cow , while the ones used for farm labour are called draught animals like ox,donkey.
The scientific name of common Indian cow is Bos indicus
5. (a) Differentiate between mixed cropping and inter-cropping. Give one example of each.
(b) How is crop-rotation different from the above two ?
(c) Mention the factors that are taken into consideration for deciding choice of crops for inter
cropping and crop rotation. Also mention one advantage of each of these cropping patterns.
Ans: (a) In mixed cropping two or more crops are grown simultaneously. For eg wheat + gram
Inter - cropping - two or more crops are grown simultaneously on the same field in a definite pattern. For eg, soyabean +maize
(b) In crop rotation different crops are grown on a piece of land in a pre-planned succession.
Depending upon duration of crop rotation is done for different crop combination.
(c) Inter- Cropping - crops are selected such that their nutrient requirements are different. This ensures maximum utilization of the nutrients supplied and prevents pests and diseases from spreading to all plants - thus better returns.
Crop - rotation - Availability of moisture and irrigation facilities Two or more crops can be grown in a year with good harvest
SA-I (2013) NK9FZA3
1. Mention the significance of sun hemp in the crop variety improvement process.1
Ans: Sun hemp is a green plant that turn into green manure which helps in enriching the soil in nitrogen and phosphorus.
2. What is organic farming? List its four advantages. 3
Ans: Organic farming is a farming system with minimal or no use of chemicals as fertilizers, herbicides, pesticides etc with a maximum input of organic manures.
Advantages:-
(a) Farm wastes (straw and livestock excreta) are recycled.
(b) Bio agents such as culture of blue green algal are used in the preparation of bio fertilizers.
(c) Neem leaves or turmeric is used as a bio pesticide in storage of grains.
(d) Healthy cropping systems such as mixed cropping inter cropping and crop rotation are beneficial in insect, pest and weed control besides providing nutrients.
3 (a) List three factors on which cultivation practices and crop yield depends.
(b) Name three stages involved in farming practices. 3
Ans: (a) Biotic and abiotic resistance, change in maturity duration, wider adaptability.
(b) Crop variety improvement, crop production improvement, crop protection management.
4. (a) Farmer A wants to grow fodder crops while farmer B wants to grow cereals. Mention the agronomic characteristics which the two farmer would desire in their respective crops. 5
(b) List any four other factors for which variety improvement is done.
(c) Name and define the process of incorporating desirable characteristics into crops.
Ans: (a) For fodder crop – Tallness and profuse branching and Cereal crop - Dwarfness
(b) Higher yield, biotic and abiotic resistance, changes in maturity duration, Improved quality, wider adaptability.
(c) Hybridization. : It is the process of crossing between genetically dissimilar plants.
SA-1(2014) LACWASE
1. India is a country with three fourth of the population engaged in agriculture. Even though financial conditions of some farmers do allow them to take higher level farming practices and improved agriculture technology, yet they are hesitant to use of HYV seeds with traits such as resistance to disease and pests, high quality that would results finally in higher yield. [3]
(i) What is meant by genetically modified crops ?
(ii) What are the desired agronomic characters for fodder and cereal crops ?
(iii) In your opinion what should be done so that the modern agriculture technology is adopted by most of the farmers ?
Ans: (i) To get desired traits in a crop (ii) Fodder – profuse branching, cereal – dwarfness
(iii) encourage scientific temper, awareness, use of knowledge
2. Define ‘Rain water Harvesting’ and ‘Water shed management’ and state one advantage of each. [3]
Ans: Rainwater harvesting is a technique used for collecting, storing and using rainwater for irrigation and other uses. The rainwater is collected from various hard surfaces such as roof tops and/or other manmade aboveground hard surfaces.
Watershed management: The management of water resources in an certain area. It is done to increase the utility of rainwater by building small check-dams . The check-dams stop the rainwater from flowing away and also reduce soil erosion.
3. ow does maximum utilization of available resources be ensured in composite fish farming ? Mention its limitation? Discuss how this limitation of composite fish culture can be overcome? [5]
Ans: The maximum utilization of available resources be ensured in composite fish farming by using of number of fish varieties in a single pond to prevent competition for resources. Each one must have different feeding zones.
Limitation – The major problem in fish farming is the lack of availability of good quality seed.
To overcome this problem, fishes are allowed to breed in ponds using hormonal stimulation. This has ensured the supply of pure fish seed in desired quantities.
4. what is hormonal stimulation in fish and how is it done in fish?
Ans: Hormonal stimulation of fishes is done to mature sex cells artificially. Hormones and methods used for stimulation slightly vary for different species of fishes. Hormone that could be used for stimulation is Luteinizing hormone (LH) that trigger ovulation.
5. In an experiment to test the presence of starch in a sample of food the wrong step is :[1]
(a) Take foodstuff like potato or rice
(b) Crush food in boiling water
(c) Add iodine powder in test tube (Ans)
(d) Pour mixture in the test tube
6. Rohit was trying to test the presence of starch in potato extract. He forgot the reagent with which starch gives blue black colour. Help him to select the correct stain from the following :[1]
(a) Safranin
(b) Methylene blue
c) Iodine solution (ans)
c) Iodine solution (ans)
(d) Eosin
7. What do you mean by the term sustainable development?
Ans: Sustainable development means to meet the needs of present generation ,without foreclosing the options of future generation, to keep balance between development and environment.
SA-1(2014) 7 EKSMTL
1. Sohnapur, a small village, where crops were dependent on rain. Villagers were at the mercy of monsoon. To prevent crop failure they discussed the matter in the panchayat and wanted to do some havan to appease Rain Gods. But Rakesh who was studying in class IX, advised all of them to adopt measures for conserving water and stop crop failure.
(i) If there is low rainfall in a village throughout the year. List at least two measures by which farmers can prevent crop failure in future.
(ii) List two traditional ways of conserving water for irrigation.
(iii) Write two values of Rakesh that have helped the villagers to sail through the difficult times. [3]
Ans: (i) enrich soil with humus to increase water holding capacity, use of drought resistant varieties
(ii) Traditional methods of irrigation involve different ways of obtaining water from wells, lakes, and canals and transporting it to fields with the help of cattle or by human labour like Dhekli, chain and pump,Moat (pully system)
(iiI) critical and analytical thinking, preparedness, cooperation, team work, mutual concern, applying knowledge.
2. Explain intensive fish farming with the help of one example . Write two advantages of this pences. [3]
Ans: Intensive fish farming or in combination with a rice crop so that fish are grown in the water in the paddy field. Both local and imported fish species are used in such system.
Advantages of this process :
(i) Maximum use of resources. (ii) Increase the yield.
3. Define ‘Hybridisation’. Explain the three types of cross-breeding practiced during hybridisation ? What do you mean by genetically modified crops ?
Ans: Hybridisation is way of crossing between genetically dissimilar plants.
a. Intervarietal Hybridization: way of crossing between different varieties
b. Interspecific Hybridization : way of crossing between different species
c. Intergeneric Hybridization : way of crossing between different genera
Genetically Modified Crops (GMC).: Another way of improving the crop is by introducing a gene that would provide the desired characteristic.
4. In a sample of food iodine solution is used to detect the presence of :
7. What do you mean by the term sustainable development?
Ans: Sustainable development means to meet the needs of present generation ,without foreclosing the options of future generation, to keep balance between development and environment.
SA-1(2014) 7 EKSMTL
1. Sohnapur, a small village, where crops were dependent on rain. Villagers were at the mercy of monsoon. To prevent crop failure they discussed the matter in the panchayat and wanted to do some havan to appease Rain Gods. But Rakesh who was studying in class IX, advised all of them to adopt measures for conserving water and stop crop failure.
(i) If there is low rainfall in a village throughout the year. List at least two measures by which farmers can prevent crop failure in future.
(ii) List two traditional ways of conserving water for irrigation.
(iii) Write two values of Rakesh that have helped the villagers to sail through the difficult times. [3]
Ans: (i) enrich soil with humus to increase water holding capacity, use of drought resistant varieties
(ii) Traditional methods of irrigation involve different ways of obtaining water from wells, lakes, and canals and transporting it to fields with the help of cattle or by human labour like Dhekli, chain and pump,Moat (pully system)
(iiI) critical and analytical thinking, preparedness, cooperation, team work, mutual concern, applying knowledge.
2. Explain intensive fish farming with the help of one example . Write two advantages of this pences. [3]
Ans: Intensive fish farming or in combination with a rice crop so that fish are grown in the water in the paddy field. Both local and imported fish species are used in such system.
Advantages of this process :
(i) Maximum use of resources. (ii) Increase the yield.
3. Define ‘Hybridisation’. Explain the three types of cross-breeding practiced during hybridisation ? What do you mean by genetically modified crops ?
Ans: Hybridisation is way of crossing between genetically dissimilar plants.
a. Intervarietal Hybridization: way of crossing between different varieties
b. Interspecific Hybridization : way of crossing between different species
c. Intergeneric Hybridization : way of crossing between different genera
Genetically Modified Crops (GMC).: Another way of improving the crop is by introducing a gene that would provide the desired characteristic.
4. In a sample of food iodine solution is used to detect the presence of :
(a) Proteins
(b) Starch (ans)
(c) Sugar
(d) Fats
(b) Starch (ans)
(c) Sugar
(d) Fats
5.Yellow brown colour is the colour of a reagent named :
(a) dil HCl
(a) dil HCl
(b) safranin
(c) Iodine solution (ans)
(c) Iodine solution (ans)
(d) dil sodium hydroxide
CLASS IX SCIENCE- FOOD RESOURCES QUESTIONS FROM CBSE PAPERS
SA-I (2013) TLPEK7V
1. Mention two climatic conditions essential for different crops for growth and completion of their life cycle. 1
Ans: Temperature and photoperiods.
2. “Green Revolution of 1960 is a boon by itself”. List three steps that may be initiated to increase crop production 3
Ans: The major groups of activities for improving crop yields can be classified as:
(a) Crop variety improvement (b)Crop production improvement (c) Crop protection management.
3. In what ways internal parasites like worms and flukes and external parasites cause harm to the cattle’s. 3
Ans: External parasite – Skin diseases; worms – affect stomach and intestine; Flukes – damage liver
4. Explain the meaning of ‘milch’ and ‘draught animals. Mention the scientific name of common Indian cow. 3
Ans: Milk-producing females are called milch animals (dairy animals) like cow , while the ones used for farm labour are called draught animals like ox,donkey.
The scientific name of common Indian cow is Bos indicus
5. (a) Differentiate between mixed cropping and inter-cropping. Give one example of each.
(b) How is crop-rotation different from the above two ?
(c) Mention the factors that are taken into consideration for deciding choice of crops for inter
cropping and crop rotation. Also mention one advantage of each of these cropping patterns.
Ans: (a) In mixed cropping two or more crops are grown simultaneously. For eg wheat + gram
Inter - cropping - two or more crops are grown simultaneously on the same field in a definite pattern. For eg, soyabean +maize
(b) In crop rotation different crops are grown on a piece of land in a pre-planned succession.
Depending upon duration of crop rotation is done for different crop combination.
(c) Inter- Cropping - crops are selected such that their nutrient requirements are different. This ensures maximum utilization of the nutrients supplied and prevents pests and diseases from spreading to all plants - thus better returns.
Crop - rotation - Availability of moisture and irrigation facilities Two or more crops can be grown in a year with good harvest
SA-I (2013) NK9FZA3
1. Mention the significance of sun hemp in the crop variety improvement process.1
Ans: Sun hemp is a green plant that turn into green manure which helps in enriching the soil in nitrogen and phosphorus.
2. What is organic farming? List its four advantages. 3
Ans: Organic farming is a farming system with minimal or no use of chemicals as fertilizers, herbicides, pesticides etc with a maximum input of organic manures.
Advantages:-
(a) Farm wastes (straw and livestock excreta) are recycled.
(b) Bio agents such as culture of blue green algal are used in the preparation of bio fertilizers.
(c) Neem leaves or turmeric is used as a bio pesticide in storage of grains.
(d) Healthy cropping systems such as mixed cropping inter cropping and crop rotation are beneficial in insect, pest and weed control besides providing nutrients.
3 (a) List three factors on which cultivation practices and crop yield depends.
(b) Name three stages involved in farming practices. 3
Ans: (a) Biotic and abiotic resistance, change in maturity duration, wider adaptability.
(b) Crop variety improvement, crop production improvement, crop protection management.
4. (a) Farmer A wants to grow fodder crops while farmer B wants to grow cereals. Mention the agronomic characteristics which the two farmer would desire in their respective crops. 5
(b) List any four other factors for which variety improvement is done.
(c) Name and define the process of incorporating desirable characteristics into crops.
Ans: (a) For fodder crop – Tallness and profuse branching and Cereal crop - Dwarfness
(b) Higher yield, biotic and abiotic resistance, changes in maturity duration, Improved quality, wider adaptability.
(c) Hybridization. : It is the process of crossing between genetically dissimilar plants.
SA-1(2014) LACWASE
1. India is a country with three fourth of the population engaged in agriculture. Even though financial conditions of some farmers do allow them to take higher level farming practices and improved agriculture technology, yet they are hesitant to use of HYV seeds with traits such as resistance to disease and pests, high quality that would results finally in higher yield. [3]
(i) What is meant by genetically modified crops ?
(ii) What are the desired agronomic characters for fodder and cereal crops ?
(iii) In your opinion what should be done so that the modern agriculture technology is adopted by most of the farmers ?
Ans: (i) To get desired traits in a crop (ii) Fodder – profuse branching, cereal – dwarfness
(iii) encourage scientific temper, awareness, use of knowledge
2. Define ‘Rain water Harvesting’ and ‘Water shed management’ and state one advantage of each. [3]
Ans: Rainwater harvesting is a technique used for collecting, storing and using rainwater for irrigation and other uses. The rainwater is collected from various hard surfaces such as roof tops and/or other manmade aboveground hard surfaces.
Watershed management: The management of water resources in an certain area. It is done to increase the utility of rainwater by building small check-dams . The check-dams stop the rainwater from flowing away and also reduce soil erosion.
3. ow does maximum utilization of available resources be ensured in composite fish farming ? Mention its limitation? Discuss how this limitation of composite fish culture can be overcome? [5]
Ans: The maximum utilization of available resources be ensured in composite fish farming by using of number of fish varieties in a single pond to prevent competition for resources. Each one must have different feeding zones.
Limitation – The major problem in fish farming is the lack of availability of good quality seed.
To overcome this problem, fishes are allowed to breed in ponds using hormonal stimulation. This has ensured the supply of pure fish seed in desired quantities.
4. what is hormonal stimulation in fish and how is it done in fish?
Ans: Hormonal stimulation of fishes is done to mature sex cells artificially. Hormones and methods used for stimulation slightly vary for different species of fishes. Hormone that could be used for stimulation is Luteinizing hormone (LH) that trigger ovulation.
5. In an experiment to test the presence of starch in a sample of food the wrong step is :[1]
(a) Take foodstuff like potato or rice
(b) Crush food in boiling water
(c) Add iodine powder in test tube (Ans)
(d) Pour mixture in the test tube
6. Rohit was trying to test the presence of starch in potato extract. He forgot the reagent with which starch gives blue black colour. Help him to select the correct stain from the following :[1]
(a) Safranin
1. Mention two climatic conditions essential for different crops for growth and completion of their life cycle. 1
Ans: Temperature and photoperiods.
2. “Green Revolution of 1960 is a boon by itself”. List three steps that may be initiated to increase crop production 3
Ans: The major groups of activities for improving crop yields can be classified as:
(a) Crop variety improvement (b)Crop production improvement (c) Crop protection management.
3. In what ways internal parasites like worms and flukes and external parasites cause harm to the cattle’s. 3
Ans: External parasite – Skin diseases; worms – affect stomach and intestine; Flukes – damage liver
4. Explain the meaning of ‘milch’ and ‘draught animals. Mention the scientific name of common Indian cow. 3
Ans: Milk-producing females are called milch animals (dairy animals) like cow , while the ones used for farm labour are called draught animals like ox,donkey.
The scientific name of common Indian cow is Bos indicus
5. (a) Differentiate between mixed cropping and inter-cropping. Give one example of each.
(b) How is crop-rotation different from the above two ?
(c) Mention the factors that are taken into consideration for deciding choice of crops for inter
cropping and crop rotation. Also mention one advantage of each of these cropping patterns.
Ans: (a) In mixed cropping two or more crops are grown simultaneously. For eg wheat + gram
Inter - cropping - two or more crops are grown simultaneously on the same field in a definite pattern. For eg, soyabean +maize
(b) In crop rotation different crops are grown on a piece of land in a pre-planned succession.
Depending upon duration of crop rotation is done for different crop combination.
(c) Inter- Cropping - crops are selected such that their nutrient requirements are different. This ensures maximum utilization of the nutrients supplied and prevents pests and diseases from spreading to all plants - thus better returns.
Crop - rotation - Availability of moisture and irrigation facilities Two or more crops can be grown in a year with good harvest
SA-I (2013) NK9FZA3
1. Mention the significance of sun hemp in the crop variety improvement process.1
Ans: Sun hemp is a green plant that turn into green manure which helps in enriching the soil in nitrogen and phosphorus.
2. What is organic farming? List its four advantages. 3
Ans: Organic farming is a farming system with minimal or no use of chemicals as fertilizers, herbicides, pesticides etc with a maximum input of organic manures.
Advantages:-
(a) Farm wastes (straw and livestock excreta) are recycled.
(b) Bio agents such as culture of blue green algal are used in the preparation of bio fertilizers.
(c) Neem leaves or turmeric is used as a bio pesticide in storage of grains.
(d) Healthy cropping systems such as mixed cropping inter cropping and crop rotation are beneficial in insect, pest and weed control besides providing nutrients.
3 (a) List three factors on which cultivation practices and crop yield depends.
(b) Name three stages involved in farming practices. 3
Ans: (a) Biotic and abiotic resistance, change in maturity duration, wider adaptability.
(b) Crop variety improvement, crop production improvement, crop protection management.
4. (a) Farmer A wants to grow fodder crops while farmer B wants to grow cereals. Mention the agronomic characteristics which the two farmer would desire in their respective crops. 5
(b) List any four other factors for which variety improvement is done.
(c) Name and define the process of incorporating desirable characteristics into crops.
Ans: (a) For fodder crop – Tallness and profuse branching and Cereal crop - Dwarfness
(b) Higher yield, biotic and abiotic resistance, changes in maturity duration, Improved quality, wider adaptability.
(c) Hybridization. : It is the process of crossing between genetically dissimilar plants.
SA-1(2014) LACWASE
1. India is a country with three fourth of the population engaged in agriculture. Even though financial conditions of some farmers do allow them to take higher level farming practices and improved agriculture technology, yet they are hesitant to use of HYV seeds with traits such as resistance to disease and pests, high quality that would results finally in higher yield. [3]
(i) What is meant by genetically modified crops ?
(ii) What are the desired agronomic characters for fodder and cereal crops ?
(iii) In your opinion what should be done so that the modern agriculture technology is adopted by most of the farmers ?
Ans: (i) To get desired traits in a crop (ii) Fodder – profuse branching, cereal – dwarfness
(iii) encourage scientific temper, awareness, use of knowledge
2. Define ‘Rain water Harvesting’ and ‘Water shed management’ and state one advantage of each. [3]
Ans: Rainwater harvesting is a technique used for collecting, storing and using rainwater for irrigation and other uses. The rainwater is collected from various hard surfaces such as roof tops and/or other manmade aboveground hard surfaces.
Watershed management: The management of water resources in an certain area. It is done to increase the utility of rainwater by building small check-dams . The check-dams stop the rainwater from flowing away and also reduce soil erosion.
3. ow does maximum utilization of available resources be ensured in composite fish farming ? Mention its limitation? Discuss how this limitation of composite fish culture can be overcome? [5]
Ans: The maximum utilization of available resources be ensured in composite fish farming by using of number of fish varieties in a single pond to prevent competition for resources. Each one must have different feeding zones.
Limitation – The major problem in fish farming is the lack of availability of good quality seed.
To overcome this problem, fishes are allowed to breed in ponds using hormonal stimulation. This has ensured the supply of pure fish seed in desired quantities.
4. what is hormonal stimulation in fish and how is it done in fish?
Ans: Hormonal stimulation of fishes is done to mature sex cells artificially. Hormones and methods used for stimulation slightly vary for different species of fishes. Hormone that could be used for stimulation is Luteinizing hormone (LH) that trigger ovulation.
5. In an experiment to test the presence of starch in a sample of food the wrong step is :[1]
(a) Take foodstuff like potato or rice
(b) Crush food in boiling water
(c) Add iodine powder in test tube (Ans)
(d) Pour mixture in the test tube
6. Rohit was trying to test the presence of starch in potato extract. He forgot the reagent with which starch gives blue black colour. Help him to select the correct stain from the following :[1]
(a) Safranin
(b) Methylene blue
c) Iodine solution (ans)
c) Iodine solution (ans)
(d) Eosin
7. What do you mean by the term sustainable development?
Ans: Sustainable development means to meet the needs of present generation ,without foreclosing the options of future generation, to keep balance between development and environment.
SA-1(2014) 7 EKSMTL
1. Sohnapur, a small village, where crops were dependent on rain. Villagers were at the mercy of monsoon. To prevent crop failure they discussed the matter in the panchayat and wanted to do some havan to appease Rain Gods. But Rakesh who was studying in class IX, advised all of them to adopt measures for conserving water and stop crop failure.
(i) If there is low rainfall in a village throughout the year. List at least two measures by which farmers can prevent crop failure in future.
(ii) List two traditional ways of conserving water for irrigation.
(iii) Write two values of Rakesh that have helped the villagers to sail through the difficult times. [3]
Ans: (i) enrich soil with humus to increase water holding capacity, use of drought resistant varieties
(ii) Traditional methods of irrigation involve different ways of obtaining water from wells, lakes, and canals and transporting it to fields with the help of cattle or by human labour like Dhekli, chain and pump,Moat (pully system)
(iiI) critical and analytical thinking, preparedness, cooperation, team work, mutual concern, applying knowledge.
2. Explain intensive fish farming with the help of one example . Write two advantages of this pences. [3]
Ans: Intensive fish farming or in combination with a rice crop so that fish are grown in the water in the paddy field. Both local and imported fish species are used in such system.
Advantages of this process :
(i) Maximum use of resources. (ii) Increase the yield.
3. Define ‘Hybridisation’. Explain the three types of cross-breeding practiced during hybridisation ? What do you mean by genetically modified crops ?
Ans: Hybridisation is way of crossing between genetically dissimilar plants.
a. Intervarietal Hybridization: way of crossing between different varieties
b. Interspecific Hybridization : way of crossing between different species
c. Intergeneric Hybridization : way of crossing between different genera
Genetically Modified Crops (GMC).: Another way of improving the crop is by introducing a gene that would provide the desired characteristic.
4. In a sample of food iodine solution is used to detect the presence of :
7. What do you mean by the term sustainable development?
Ans: Sustainable development means to meet the needs of present generation ,without foreclosing the options of future generation, to keep balance between development and environment.
SA-1(2014) 7 EKSMTL
1. Sohnapur, a small village, where crops were dependent on rain. Villagers were at the mercy of monsoon. To prevent crop failure they discussed the matter in the panchayat and wanted to do some havan to appease Rain Gods. But Rakesh who was studying in class IX, advised all of them to adopt measures for conserving water and stop crop failure.
(i) If there is low rainfall in a village throughout the year. List at least two measures by which farmers can prevent crop failure in future.
(ii) List two traditional ways of conserving water for irrigation.
(iii) Write two values of Rakesh that have helped the villagers to sail through the difficult times. [3]
Ans: (i) enrich soil with humus to increase water holding capacity, use of drought resistant varieties
(ii) Traditional methods of irrigation involve different ways of obtaining water from wells, lakes, and canals and transporting it to fields with the help of cattle or by human labour like Dhekli, chain and pump,Moat (pully system)
(iiI) critical and analytical thinking, preparedness, cooperation, team work, mutual concern, applying knowledge.
2. Explain intensive fish farming with the help of one example . Write two advantages of this pences. [3]
Ans: Intensive fish farming or in combination with a rice crop so that fish are grown in the water in the paddy field. Both local and imported fish species are used in such system.
Advantages of this process :
(i) Maximum use of resources. (ii) Increase the yield.
3. Define ‘Hybridisation’. Explain the three types of cross-breeding practiced during hybridisation ? What do you mean by genetically modified crops ?
Ans: Hybridisation is way of crossing between genetically dissimilar plants.
a. Intervarietal Hybridization: way of crossing between different varieties
b. Interspecific Hybridization : way of crossing between different species
c. Intergeneric Hybridization : way of crossing between different genera
Genetically Modified Crops (GMC).: Another way of improving the crop is by introducing a gene that would provide the desired characteristic.
4. In a sample of food iodine solution is used to detect the presence of :
(a) Proteins
(b) Starch (ans)
(c) Sugar
(d) Fats
(b) Starch (ans)
(c) Sugar
(d) Fats
5.Yellow brown colour is the colour of a reagent named :
(a) dil HCl
(a) dil HCl
(b) safranin
(c) Iodine solution (ans)
(c) Iodine solution (ans)
(d) dil sodium hydroxide
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
