Class IX: Chapter 5 (Natural Vegetation and Wildlife) Question & Answer
Answer the following questions briefly
Q1. Define an ecosystem.
Ans: All the plants and animals in an area are interdependent on each other. The plants and animals, alongwith their physical environment make the ecosystem. Interrelation between plants and animals in the natural environment is called Ecosystem.
Ans: All the plants and animals in an area are interdependent on each other. The plants and animals, alongwith their physical environment make the ecosystem. Interrelation between plants and animals in the natural environment is called Ecosystem.
Q2. What factors are responsible for the distribution of plants and animals in India?
Ans: Factors responsible for the distribution of plants and animals in India are:
(a) Relief: Land and soil
(b) Climate: Temperature, Humidity, Photoperiod and Precipitation.
Ans: Factors responsible for the distribution of plants and animals in India are:
(a) Relief: Land and soil
(b) Climate: Temperature, Humidity, Photoperiod and Precipitation.
Q3. What is a bio-reserve? Give two examples.
Ans: Bio-reserves are the large areas where vegetation, wildlife and the environment are conserved to preserve the biological diversity. In totality there are 14 bio-reserves in India. For e.g. Sunderbans Bio-reserve in West Bengal and Nanda Devi Bio-reserve in Uttaranchal.
Ans: Bio-reserves are the large areas where vegetation, wildlife and the environment are conserved to preserve the biological diversity. In totality there are 14 bio-reserves in India. For e.g. Sunderbans Bio-reserve in West Bengal and Nanda Devi Bio-reserve in Uttaranchal.
Q4. Name two animals having habitat in tropical and montane type of vegetation.
Ans: Animals found in tropical vegetations are: Elephant and Deer. Animals found in montane vegetations are: Snow Leopard and Yak.
Ans: Animals found in tropical vegetations are: Elephant and Deer. Animals found in montane vegetations are: Snow Leopard and Yak.
Q5. Distinguish between.
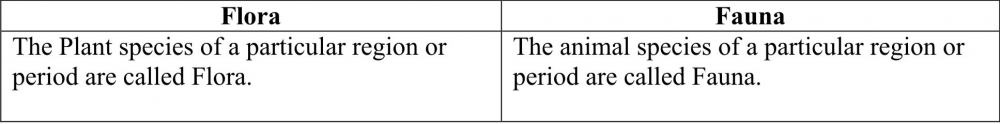
(a) Flora and Fauna
(b) Tropical Evergreen and Deciduous Forests
Ans:
(a)
(a) Flora and Fauna
(b) Tropical Evergreen and Deciduous Forests
Ans:
(a)
(b)
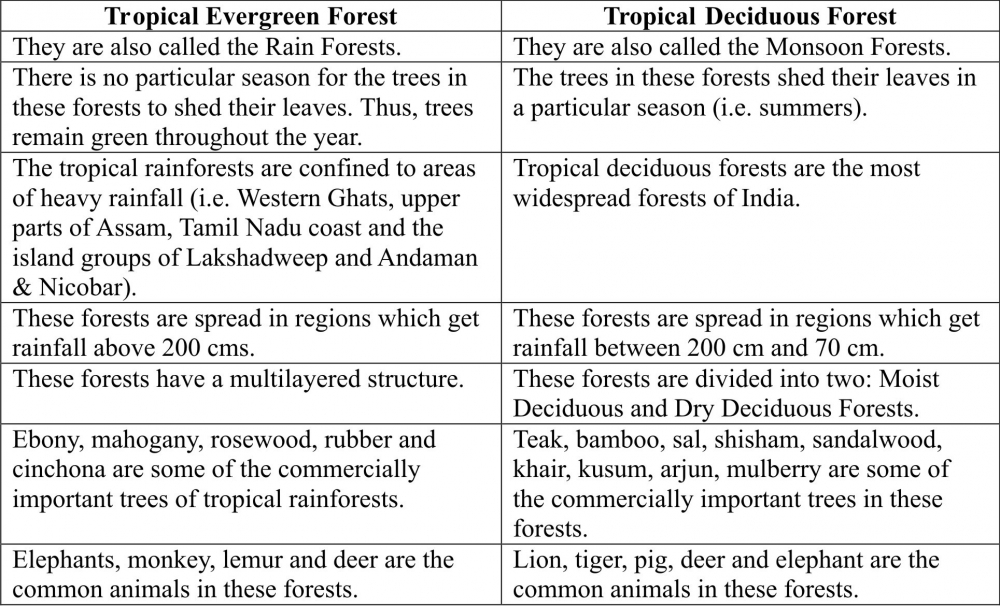
Q6. Name different types of Vegetation found in India and describe the vegetation of high altitudes.
Ans: There are five major types of vegetation in India: Tropical Rainforests, Tropical Deciduous Forests, Tropical Thorn Forests and Scrubs, Montane Forests and Mangrove Forests.
Ans: There are five major types of vegetation in India: Tropical Rainforests, Tropical Deciduous Forests, Tropical Thorn Forests and Scrubs, Montane Forests and Mangrove Forests.
Montane Forest:
• The forests in the mountainous areas are called montane forest.
• Different types of vegetation are found at different altitudes in the mountains.
(a) The wet temperate type of forest is found between a height of 1000 and 2000 meters. Evergreen broad-leaf trees such as oak and chestnut abound in such forests.
(b) Temperate forests are found between the heights of 1500 and 3000 meters. Coniferous trees; like pine, deodar, silver fir, spruce and cedar abound in such forests.
(c) Alpine vegetation (temperate forest and grasslands) are found at a height of more than 3600 meters. Silver fir, junipers, pines and birches are the common trees found here.
(d) Above alpine vegetations found are the shrubs and scrubs used for grazing of animals by the nomadic tribes (i.e. Gujjars and Bakarwals).
(e) At the higher altitude Tundra vegetations are found. mosses and lichens are found here.
• Kashmir stag, spotted deer, wild sheep, jack rabbit, Tibetan antelope, yak, snow leopard, squirrels, Shaggy horn wild ibex, bear, rare red panda, sheep and goats are the common animals in these forests.
• The forests in the mountainous areas are called montane forest.
• Different types of vegetation are found at different altitudes in the mountains.
(a) The wet temperate type of forest is found between a height of 1000 and 2000 meters. Evergreen broad-leaf trees such as oak and chestnut abound in such forests.
(b) Temperate forests are found between the heights of 1500 and 3000 meters. Coniferous trees; like pine, deodar, silver fir, spruce and cedar abound in such forests.
(c) Alpine vegetation (temperate forest and grasslands) are found at a height of more than 3600 meters. Silver fir, junipers, pines and birches are the common trees found here.
(d) Above alpine vegetations found are the shrubs and scrubs used for grazing of animals by the nomadic tribes (i.e. Gujjars and Bakarwals).
(e) At the higher altitude Tundra vegetations are found. mosses and lichens are found here.
• Kashmir stag, spotted deer, wild sheep, jack rabbit, Tibetan antelope, yak, snow leopard, squirrels, Shaggy horn wild ibex, bear, rare red panda, sheep and goats are the common animals in these forests.
Q7. Quite a few species of plants and animals are endangered in India. Why?
Ans: Species of some plants and animals are on the verge of extinction as their population has decreased considerably. Such species are known as "Endangered Species".
Following are the reasons behind species becoming endangered:
(a) Increase in population.
(b) Urbanization and Industrialization.
(c) Large scale deforestation.
(d) Pollution.
(e) Hunting for pleasure and commercial purpose, etc.
Ans: Species of some plants and animals are on the verge of extinction as their population has decreased considerably. Such species are known as "Endangered Species".
Following are the reasons behind species becoming endangered:
(a) Increase in population.
(b) Urbanization and Industrialization.
(c) Large scale deforestation.
(d) Pollution.
(e) Hunting for pleasure and commercial purpose, etc.
Q8. Why has India a rich heritage of flora and fauna?
Ans: India has a rich heritage of flora and fauna due to the following reasons:
(a) India is a diverse country with different relief features (i.e. mountains, plateaus, plains, etc.) Different types of vegetations are found in these regions and the vegetations support different type of animals.
(b) Availability of different types of soil providing base for different type of vegetations.
(c) Variation in the climatic conditions (Temperature, humidity, etc.). Climate of India differs from north to south and east to west. Thus, supporting large variety of flora and fauna.
(d) India has a monsoon type of climate where rainfall varies from 20 cms to 300 cms distributed through out the year supporting large amount of flora and fauna.
(e) Variation in the duration of sunlight at different places due to difference in the latitude and altitude.
Ans: India has a rich heritage of flora and fauna due to the following reasons:
(a) India is a diverse country with different relief features (i.e. mountains, plateaus, plains, etc.) Different types of vegetations are found in these regions and the vegetations support different type of animals.
(b) Availability of different types of soil providing base for different type of vegetations.
(c) Variation in the climatic conditions (Temperature, humidity, etc.). Climate of India differs from north to south and east to west. Thus, supporting large variety of flora and fauna.
(d) India has a monsoon type of climate where rainfall varies from 20 cms to 300 cms distributed through out the year supporting large amount of flora and fauna.
(e) Variation in the duration of sunlight at different places due to difference in the latitude and altitude.

No comments:
Post a Comment